m6A Editing: Harnessing CRISPR-Cas for Programmable RNA Modification
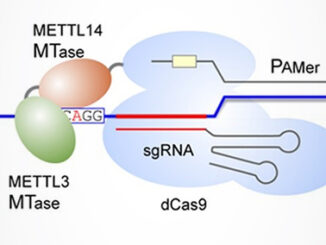
“The fifth RNA base” N6-methyladenosine, or m6A, is the most common and abundant eukaryotic RNA modification, accounting for over 80% of all RNA methylation. It can be found mainly in mRNA, but is also observed in non-coding species like tRNA, rRNA, and miRNA. Through interactions with various binding proteins called “readers”, m6A affects virtually every facet of ribonucleic acid biology: structure, splicing, localization, translation, stability, and turnover [1]. Aside from this central role in RNA metabolism, m6A is a factor [more…]