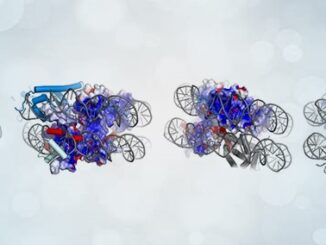
Synergistic Epigenetic Medications Show Promise in Colorectal Cancer and Beyond
Colorectal cancer ranks as the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States, presenting a multifaceted challenge influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Despite advancements in treatment, there remains a pressing need for innovative therapies, particularly as cases rise among younger adults and at advanced disease stages. One promising approach lies in epigenetics, the study of chemical modifications on DNA and its packaging proteins that influence gene expression without altering the DNA sequence. Cancer cells often display [more…]