Epigenetic Changes in Immune Cells Linked to Alzheimer’s Disease
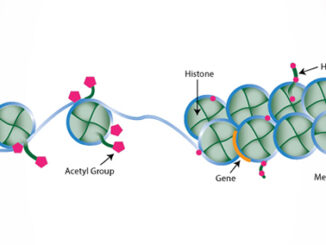
Alzheimer’s disease is a degenerative brain disorder that impacts millions globally. While the exact cause of the disease is still unknown, a recent study by Northwestern University (NU) has shed light on the potential role of epigenetic modifications in the immune system of Alzheimer’s patients. The study found that Alzheimer’s patients experience epigenetic changes in their blood’s immune system, which could be influenced by environmental factors, past infections, and lifestyle behaviors. These findings could pave the way for the development [more…]